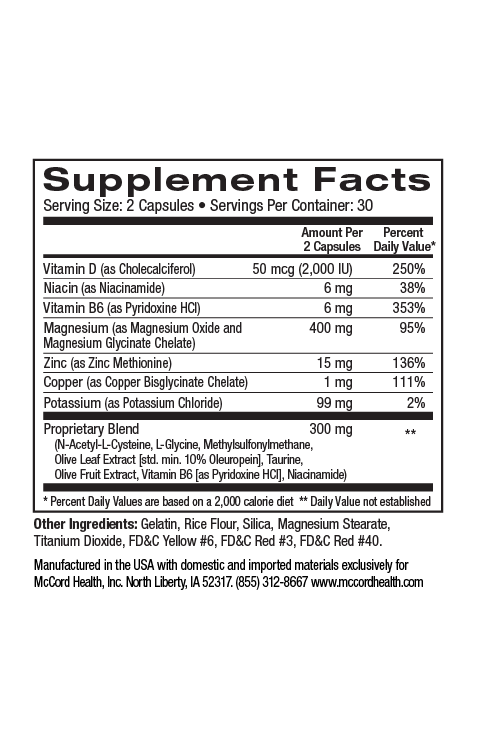
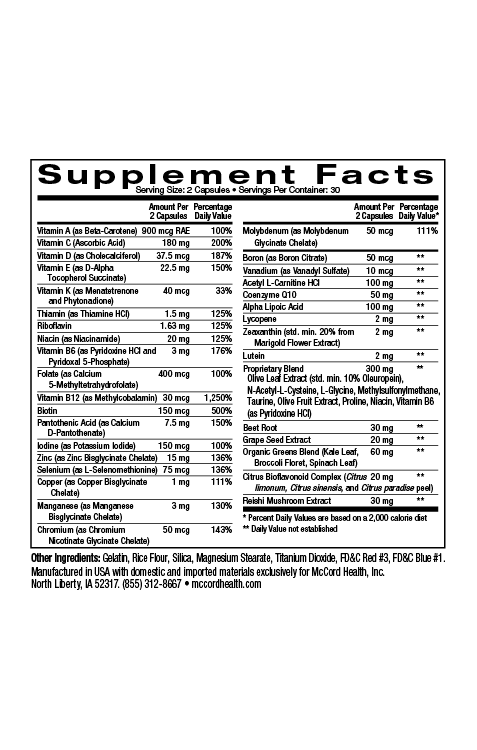
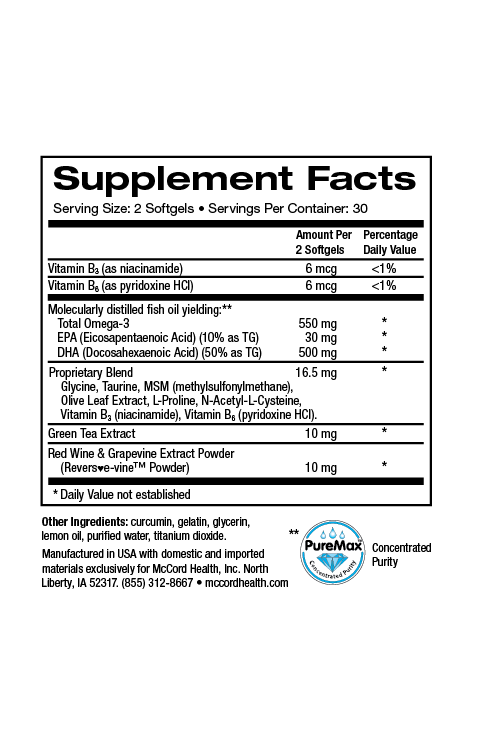
Arthritis can be debilitating due to joint irritation, inflammation and discomfort. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis both involve joint inflammation and cartilage degeneration. Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) with a high content of polyphenols including hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein was shown to prevent inflammation and cartilage degradation. In addition, an olive leaf extract that contained high levels of hydroxytyrosol prevented cartilage degeneration. Hydroxytyrosol was also shown to prevent increases in OA markers, and in another study oleuropein was able to restore cartilage regeneration. In addition to hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein, Proprietary Blend and JointHealth contain several beneficial molecules that can help decrease inflammation and oxidative stress associated with RA and OA, including curcumin.
- Joint irritation and damage can lead to arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) are more common forms of arthritis
- Both RA and OA are characterized by joint inflammation and cartilage degeneration
- EVOO with a high content of olive polyphenols including hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein was shown to prevent inflammation and cartilage degradation
- Hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein along with several other beneficial molecules in Proprietary Blend as well as curcumin (also found in JointHealth) decrease inflammation and oxidative stress associated with RA and OA
- Moreover, studies indicate that both hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein can directly improve joint cell health
There are many reasons for joint pain including joint irritation or damage that can lead to arthritis. Two more common forms of arthritis are rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA). RA is a chronic autoimmune disease where matrix enzymes (matrix metalloproteinases; MMPs) produced by cells known as synovial fibroblasts (SFs) that are found in the membrane surrounding cartilage (synovium), degrade joint cartilage and underlying bone1,2. OA is the most common form of degenerative joint disease, and it involves abnormal joint metabolism, cartilage degradation and bone remodeling3.
Joint Pain is Often a Sign that a Joint is Inflamed
Joint pain is often a sign that a joint is inflamed, which can happen with joint irritation or damage. Both rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are characterized by inflammation. In RA, the SFs produce inflammatory signaling molecules (cytokines) that induce proliferation of SFs and their invasion into surrounding tissues2. In OA, inflammation of the synovium contributes to the dysfunction of cells (chondrocytes) that produce cartilage matrix (consisting mainly of collagen, proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans including hyaluronic acid). In fact, OA is characterized by an irreversible loss of cartilage4,5.
Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) has a higher content of olive polyphenols such as hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein and has been shown to prevent inflammation and cartilage degradation in a model of RA2. In addition, a polyphenol extract of EVOO decreased inflammation, SF cell migration and bone erosion in a separate study involving this model of RA6. Further, in another important study, a phenolic extract of EVOO was found to inhibit the inflammatory response of activated SFs1. Proprietary Blend found in Pinnaclife® Joint Health includes the potent anti-inflammatory olive polyphenols, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein as well as other powerful anti-inflammatory small molecules such as methylsulfonylmethane (MSM), taurine, and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) to help decrease joint discomfort7-11.
Olive Polyphenols Help Reduce Cartilage Degeneration
EVOO was also shown to prevent cartilage degeneration in a model of OA that included mild physical activity12. Importantly, hydroxytyrosol has been shown to inhibit cartilage inflammatory responses in chondrocytes5,13. In another study, hydroxytyrosol prevented an increase in OA markers in human chondrocytes4. Olive leaf extract with a high concentration of hydroxytyrosol, was shown to prevent cartilage degeneration by increasing levels of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid in a model of OA14. OA is more prevalent in older adults and inflammation related to aging (inflammaging) is especially associated with chondrocytes that have become senescent (non-replicating)15. Oleuropein was shown to reduce senescence in chondrocytes and restore cartilage regeneration16.
In addition, hydroxytyrosol was shown to prevent chondrocyte death during oxidative stress in a model of OA17. Oxidative stress that is associated with inflammation, results from the inability of cells to eliminate free radicals known as reactive oxygen species (ROS) using the natural defense system that includes defense enzymes such as superoxide dismutases (SODs)18. Aging-associated changes in joint cartilage as well as mechanical and metabolic stress can lead to increased levels of ROS and oxidative stress that contributes to chondrocyte damage and their decreased ability to produce cartilage matrix17.
Besides hydroxytyrosol, many of the potent anti-inflammatory molecules found in Proprietary Blend can decrease oxidative stress including oleuropein, NAC, taurine and MSM19-23. Importantly, hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein, and NAC have been shown to activate (Mn)SOD that helps counteract oxidative stress24. RA studies have correlated oxidative stress with markers of oxidative damage in synovial fluid. Moreover, in patients with RA, immune cells in peripheral blood have displayed enhanced production of ROS as well as decreased ability to eliminate free radicals that led to protein damage and disease progression27.
In addition to the potent beneficial molecules of Proprietary Blend http://www.olivamine.com, the powerful molecule curcumin is included in JointHealth. Curcumin possesses additional antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities28 that also help decrease joint discomfort. Pinnaclife® JointHealth includes impeccably sourced ingredients that have undergone rigorous scientific review to prove they renew, restore and repair cells.
References
- Br J Nutr 2019; 121: 55-62.
- Eur J Nutr 2016; 55: 315-325.
- Nutrients 2017; 9: 1060, 1-18.
- PLOS One 2014; 9(10): e109724, 1-9.
- Mol Med Rep 2018; 17(3): 4035-4042.
- J Nutr Biochem 2013; 24: 1275-1281.
- Planta Med 2011; 77: 1890-1897.
- Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: 18508-18524.
- Biochem Biophys Res Comm 2104; 466: 1225-1230.
- Biol Pharm Bull 2009; 32: 651-656.
- Amino Acids 1996; 10: 59-71.
- J Nutr Biochem 2013; 24: 2064-2075.
- Int J Mol Med 2019; doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4300.
- Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2018; 82(7): 1101-1106.
- Ageing Res Rev 2017; 40: 20-30.
- BioRxiv 2019; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/686535.
- Biochim Biophys Acta 2016; 1860: 1181-1191.
- Curr Neuropharmacol 2009; 7: 65-74.
- J Agric Food Chem 2011; 59: 4473-4482.
- Sci Pharm 2010; 78: 133-154.
- Life Sci 2015; 121: 110-116.
- Amino Acids 2004; 26: 203-207.
- Cancer Res 2007; 67: 6392-6399.
- Age 2012; 34: 95-109.
- J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2014; 28: 105-116.
- Free Rad Res 2019; 53(7): 768-779.
- Neurochem Res 2014; 39(7): 1322-1331.