Cardiovascular disease is common in adults over 55 years of age and encompasses a large range of disease forms including hypertension and cardiotoxicity. Chronic inflammation and endothelial dysfunction are important processes involved in cardiovascular diseases. Chronic inflammation is also associated with obesity and diabetes that are linked with cardiovascular disease and oxidative stress. Proprietary Blend and Pinnaclife® HeartHealth include many ingredients with powerful activities against inflammation as well as oxidative stress. Endothelial dysfunction that contributes to arterial stiffness is present in various forms of cardiovascular disease including atherosclerosis. Various ingredients found in Proprietary Blend and HeartHealth have activities against hypertension, chemotherapy drug-induced cardiotoxicity, and/or help regulate calcium levels to protect heart cells and mitochondria that are critical for heart cell functioning.
- Many older adults have at least one form of cardiovascular disease
- Inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction are important processes involved in cardiovascular disease
- Proprietary Blend and Pinnaclife® HeartHealth include various ingredients that can decrease inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction
- Several ingredients found in Proprietary Blend and HeartHealth also protect against hypertension and/or chemotherapy drug-induced cardiotoxicity
- In addition, key Proprietary Blend and HeartHealth ingredients help regulate calcium levels that are critical for proper heart cell functioning
Approximately 70% of adults age 55 years and older have at least one form of cardiovascular disease1. Cardiovascular disease encompasses a large range of complex disease forms that include hypertension (high blood pressure), atherosclerosis, stroke, myocardial infarction, drug-induced cardiomyopathies, and arterial disease. There are many causes for the various forms of cardiovascular disease, however, there are some common processes that all forms tend to include such as inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and metabolic impairments associated with metabolic syndrome, obesity, and/or dyslipidemia2,3.
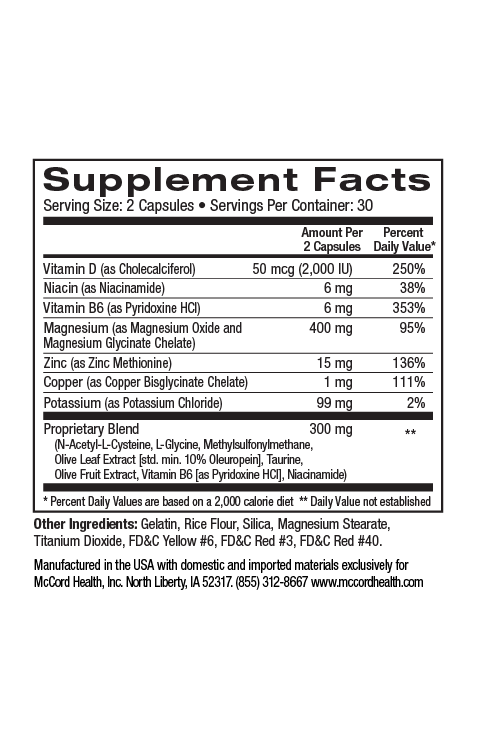
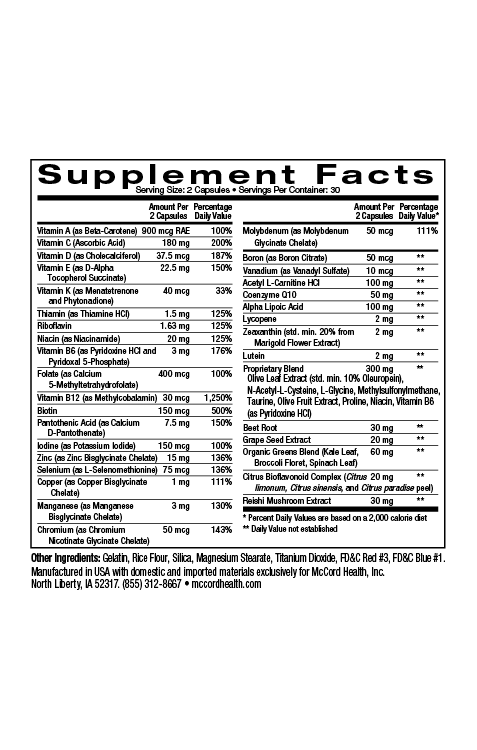
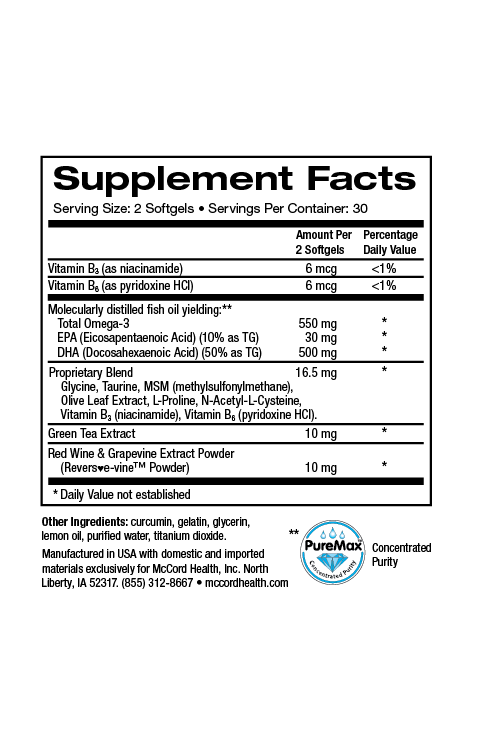
The metabolic syndrome that includes obesity and glucose intolerance (that can lead to diabetes) is linked with cardiovascular disease. An important common factor associated with the metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease is chronic inflammation4,5. Pinnaclife® HeartHealth contains Proprietary Blend that includes many beneficial ingredients that help decrease inflammation such as the potent olive polyphenols hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein as well as methylsulfonylmethane (MSM), N-acetylcysteine (NAC), and taurine6-10. Importantly, HeartHealth includes omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin that are also anti-inflammatory11,12.
Chronic inflammation can be tracked by measuring biomarkers like the acute phase protein, C-reactive protein (CRP) that can be detected in the blood. Higher CRP levels have been associated with cardiovascular disease and diabetes13,14. Interestingly, hydroxytyrosol treatment reduced levels of CRP in different models of diabetes14. Oral treatment with NAC has been shown to reduce CRP levels15 and importantly, omega-3 fatty acids found in HeartHealth have been shown to lower levels of CRP16,17. In addition, curcumin has been reported to lower production of CRP18 and treatment of patients with the combination of hydroxytyrosol, omega-3 fatty acids, and curcumin resulted in decreased levels of CRP19.
As mentioned, there are many causes for the various forms of cardiovascular disease, however, there are some common processes besides inflammation that all forms tend to include such as endothelial dysfunction and metabolic impairments associated with metabolic syndrome, obesity, and/or dyslipidemia2,3. In fact, endothelial dysfunction is present in various forms of cardiovascular disease including atherosclerosis20. Endothelial dysfunction contributes to arterial stiffness21. Free radicals known as reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can result in oxidative stress play a critical role in endothelial dysfunction that contributes to atherosclerosis development and cardiovascular disease22.
Various ingredients found in Proprietary Blend have potent antioxidant activity including hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein, NAC, MSM, and taurine23-27. Hydroxytyrosol has been shown to reduce ROS levels in vascular endothelial cells28. It has also been found to decrease endothelial dysfunction29, and hydroxytyrosol has been shown to protect against endothelial dysfunction in human aortic endothelial cells30. In addition, oleuropein was found to restore endothelial progenitor cell function31, taurine was demonstrated to protect against endothelial dysfunction32,33, and evidence suggests that N-acetyl-L-cysteine and curcumin can improve endothelial dysfunction34.
Oleuropein is well known for its beneficial activities against hypertension. In fact, clinical trials have shown that oleuropein consumption reduced blood pressure in both pre-hypertensive subjects as well in a model of high blood pressure35. Other studies also suggest that oleuropein represents a promising option to prevent and treat high blood pressure36. MSM has also been shown to reduce pulmonary arterial hypertension in a model of high blood pressure37. In addition, taurine supplementation has been shown to have antihypertensive effects and NAC was demonstrated to inhibit pulmonary arterial hypertension in a model of high blood pressure38,39.
Various drugs, including chemotherapy drugs, can produce toxic effects in heart cells (cardiotoxicity) that can lead to heart damage. Increasing evidence indicates that chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity involves oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, and increased calcium influx40. Hydroxytyrosol has been shown to decrease oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in a model of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity41. Interestingly, oleuropein has been found to prevent doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy42. In addition, taurine was shown to protect against cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity43 and NAC decreased heart cell damage and functional changes in a model of cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity44.
Notably, calcium signaling is important for heart cell function and heart failure involves dysregulated calcium levels45. Curcumin has been shown to inhibit heart cell damage and heart failure by affecting calcium levels through changes in calcium associated molecules20. In addition, taurine has been shown to protect against calcium-induced cardiac injury by preventing calcium overload and cell death in heart cells46. Calcium uptake by mitochondria is also critical for heart cell functions47. Oxidative stress and aging decrease mitochondrial functions and cellular health. Hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein, and NAC have been shown to increase activity of the antioxidant defense enzyme SOD that can protect mitochondria from damage48-50.
Proprietary Blend http://www.olivamine.com in Pinnaclife® HeartHealthhttps://pinnaclife.com/product/hearthealth/ includes many beneficial ingredients to improve heart health. Only the highest quality ingredients are provided in Proprietary Blend and HeartHealth including omega-3 fatty acids from pure fish oil. Pinnaclife® HeartHealth with Proprietary Blend includes impeccably sourced ingredients that have undergone rigorous scientific review to prove that they renew, restore, and repair cells.
References
- Curr Opin Nutr Metab Care 2019; 22: 459-464.
- Vascul Pharmacol 2015; 71: 40-56.
- J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89(6): 2595-2600.
- Nutrients 2017; 9: 306, 1-18.
- J Nat Sci 2017; 3(4): 1-22.
- Planta Med 2011; 77: 1890-1897.
- Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: 18508-18524.
- Biochem Biophys Res Comm 2104; 466: 1225-1230.
- Biol Pharm Bull 2009; 32: 651-656.
- Amino Acids 1996; 10: 59-71.
- Foods 2017; 6(10):92: 1-11.
- Food Funct 2018; 9: 3576-3596.
- Nat Rev Cardiol 2017; 14(5): 314, 1-12.
- Antioxidants 2019; 8: 188, 1-20.
- J Nephropathol 2018; 7(4); 268-272.
- Nutr Clin Pract. 2009;24(4):508-512.
- Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;104(2):280-287.
- Nitric Oxide 2003; 8: 231-234.
- Clin Transl Oncol 2019; 21(4): 489-498.
- Biotechnol Adv 2019; doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.01.010, 1-15.
- Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2019; 22: 459-464.
- Eur J Pharmacol 2011; 660(2-3): 275-282.
- J Agric Food Chem 2011; 59: 4473-4482.
- Sci Pharm 2010; 78: 133-154.
- Amino Acids 2004; 26: 203-207.
- Nutrients 2017; 9(3): 290, 1-21.
- Life Sci 2015; 121: 110-116.
- Eur J Pharmacol 2011; 660(2-3): 275-282.
- Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018; ID 9086947, 1-14.
- Mol Nutr Food Res 2015; 59(12): 2523-2536.
- Phytomed 2013; 20: 1088-1094.
- Redox Biol 2014; 2: 971-977.
- Biomed Res 2011; 32: 187-193.
- Transl Psychiatry 2015; 5(1): e492.
- Oncotarget 2017; 8: 17409.
- Neuropharmacol 2017; 113: 556-566.
- Adv Pharmacol Sci 2012; ID 507278, 1-6.
- Hypertension 2016; 67: 541-549.
- Exp Ther Med 2018; 15: 5503-5509.
- Front Pharmacol 2018; 9: 1374, 1-9.
- Biochem Pharmacol 2014; 90: 25-33.
- J Mol Cell Cardiol 2014; 69: 4-16.
- BioFactors 2016; 42(6): 647-664.
- Bratisl Lek Listy 2019; 120(6): 423-428.
- Int J Mol Sci 2018; 19(4): 1086, 1-14.
- Exp Clin Cardiol 2008; 13(20; 57-65.
- PNAS 2013; 110(26):10479-86.
- Age 2012; 34: 95-109.
- J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2014; 28: 105-116.
- Cancer Res 2007; 67: 6392-6399.