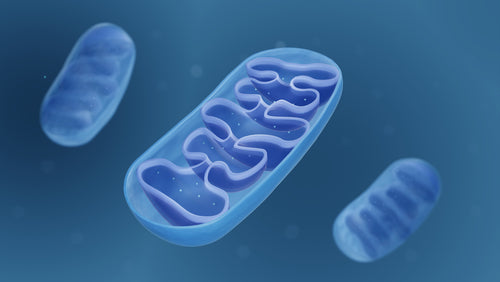
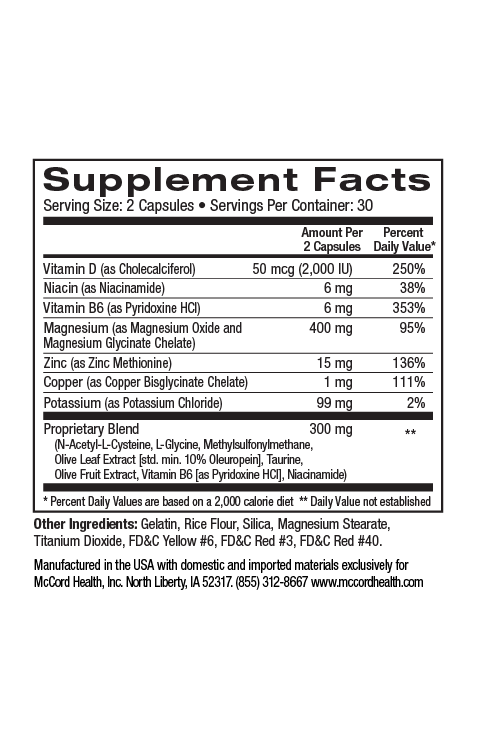
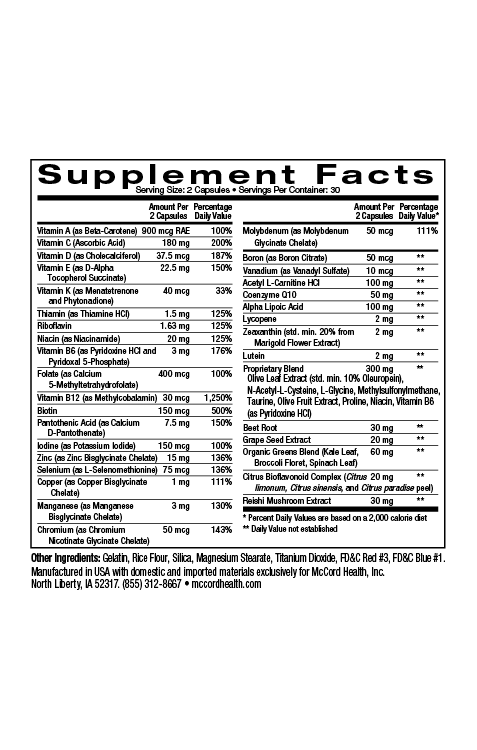
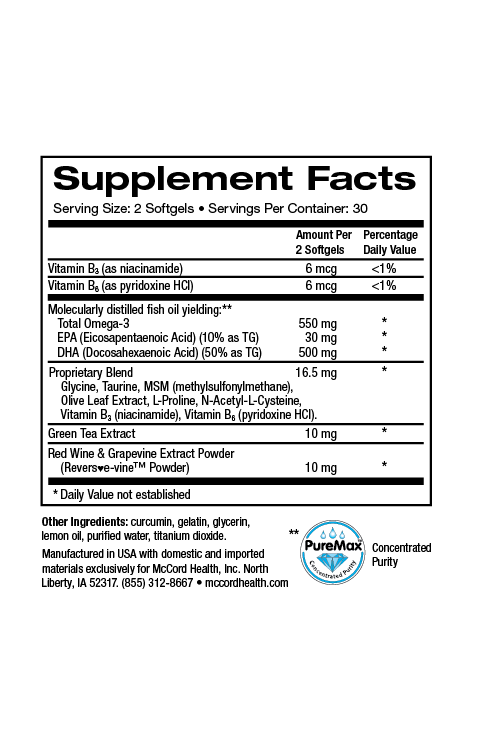
In order for cells to have enough energy to function properly, their power stations (mitochondria) must function properly. Dysfunctional mitochondria are associated with decreased energy and increased oxidative stress and inflammation that have been linked with many chronic diseases. Pinnaclife® EnergyBoost with Proprietary Blend includes various beneficial ingredients that can counteract oxidative stress and reduce inflammation associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. In many studies modeling various diseases, the potent olive polyphenols hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein have been shown to prevent or decrease mitochondrial dysfunction and promote proper mitochondrial functioning including mitochondrial biogenesis. In fact, the results from different studies suggest that decreasing mitochondrial dysfunction may decrease the risk of chronic diseases including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular, and neurological diseases.
- Mitochondria produce energy for cells to function properly
- Dysfunctional mitochondria are associated with many conditions and diseases
- Oxidative stress and inflammation are linked with mitochondrial dysfunction
- Pinnaclife® EnergyBoost with Proprietary Blend includes many ingredients that can counteract oxidative stress and help decrease inflammation
- The potent olive polyphenols hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein in Proprietary Blend can decrease mitochondrial dysfunction, increasing the health of cells and decreasing the risk of disease
Mitochondria are the organelles that produce energy for cells in the form of ATP. In order for mitochondria to make the proper amount of energy that cells need to be healthy, mitochondria must also be healthy and functioning normally1. Mitochondrial dysfunction has been associated with many conditions and diseases including aging2, metabolic syndrome3, obesity4, diabetes5, and cardiovascular disease6, as well as neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease7. When excessive free radicals known as reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced by mitochondria during energy metabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation can occur5,8. In fact, oxidative stress and inflammation are associated with mitochondrial dysfunction that is linked with less energy production9.
Hydroxytyrosol and Oleuropein Decrease Mitochondrial Dysfunction
The potent olive polyphenols hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein found in Pinnaclife® EnergyBoost with Proprietary Blend have been shown to decrease mitochondrial dysfunction. Regular exercise can increase mitochondrial numbers in skeletal muscle, however, strenuous or excessive exercise can cause damage to muscles, as well as mitochondrial breakdown (fission). Hydroxytyrosol has been shown to inhibit mitochondrial fission during excessive exercise10. In addition, in another important study, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein, as well as olive leaf extracts containing these polyphenols, protected heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) from toxin-induced cell death characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction11.
Excessive ROS can lead to oxidative stress that can damage mitochondria so that they become dysfunctional5,8. Moreover, damaged or dysfunctional mitochondria can result in increased oxidative stress12,13. Proprietary Blend in EnergyBoost includes many powerful antioxidants including hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein, as well as N-acetylcysteine (NAC), taurine and methylsulfonlymethane (MSM)14-18. Studies have shown that taurine’s antioxidant activity contributes to improved mitochondrial function12,13. Hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein, and NAC have been found to activate an important antioxidant defense enzyme, manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) that helps protect mitochondria from oxidative stress19-21. In fact, MnSOD activity has also been shown to protect mitochondria from age-associated abnormalities8.
In addition, hydroxytyrosol has been shown to be protective against mitochondrial dysfunction in a model that involved toxin-induced learning and memory impairment as well as deficits in spatial learning7. In another important study, a diet rich in purified olive polyphenols including hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein had long-term positive effects on cognition and energy metabolism suggesting substantial improvements in a model of aging that included mitochondrial dysfunction22. In addition, hydroxytyrosol protected against mitochondrial dysfunction in a model that involved toxin-induced oxidative stress in epithelial cells23.
Hydroxytyrosol Promotes Mitochondrial Function
Further, in a study that involved fat cells, hydroxytyrosol promoted mitochondrial production (biogenesis) and mitochondrial function, suggesting that hydroxytyrosol may help prevent obesity and diabetes4. Another interesting study demonstrated that hydroxytyrosol decreased mitochondrial dysfunction in a model of toxin-induced heart damage6. Hydroxytyrosol also prevented mitochondrial dysfunction in vascular endothelial cells and promoted mitochondrial biogenesis in a separate study suggesting that hydroxytyrosol could potentially target mitochondria in inflamed endothelium that are often associated with cardiovascular disease24.
Inflammation is also associated with fatigue25, obesity, diabetes, and other chronic diseases besides cardiovascular disease including neurological diseases26-29. Proprietary Blend http://www.olivamine.com found in EnergyBoost contains anti-inflammatory ingredients including hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein, MSM, NAC, and taurine30-34. In addition, resveratrol found in grape extracts included in EnergyBoost, has anti-inflammatory properties35 and rhodiola rosea also found in EnergyBoost has anti-inflammatory components36. EnergyBoost includes impeccably sourced ingredients that have undergone rigorous scientific review to prove we renew, restore, and repair cells.
References
- Nature Cell Biol 2018; 20: 735.
- J Int Med 2008; 263: 167-178.
- Biochim Biophys Acta 2017; 1863: 1132-1146.
- J Nutr Biochem 2010; 21: 634-644.
- Mediators Inflamm 2013; 2013: ID135698, 1-13.
- Biochem Pharmacol 2014; 90: 25-33.
- J Biochem Mol Toxicol 2017; 0: e21906, 1-7.
- Mitochondrion 2010; 10(4): 342-349.
- Molecules 2016; 21: 163, 1-30.
- Free Rad Biol Med 2011; 50: 1437-1446.
- Planta Med 2014; 80: 984-992.
- J Cell Sci 2006; 119: 2855-2862.
- Curr Neuropharmacol 2009; 7: 65-74.
- J Agric Food Chem 2011; 59: 4473-4482.
- Sci Pharm 2010; 78: 133-154.
- Amino Acids 2004; 26: 203-207.
- Nutrients 2017; 9(3): 290:1-21.
- Life Sci 2015; 121: 110-116.
- Age 2012; 34: 95-109.
- J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2014; 28: 105-116.
- Cancer Res 2007; 67: 6392-6399.
- Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018; 2018: ID4070935, 1-10.
- J Neurochem 2007; 103: 2690-2700.
- Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018; 2018: ID9086947, 1-14.
- Arthritis Res Technol 2015; 17: 254, 1-10.
- Curr Opin Rheumatol 2015; 27: 249-255.
- Curr Opin Rheumatol 2015; 27: 289-294.
- Mol Cells 2014; 37: 441-448.
- Free Radic Biol Med 2010; 49: 1603-1616.
- J Agric Food Chem 2011; 59: 4473-4482.
- Sci Pharm 2010; 78: 133-154.
- Amino Acids 2004; 26: 203-207.
- Nutrients 2017; 9(3): 290, 1-21.
- Life Sci 2015; 121: 110-116.
- Diab Vasc Dis Res 2014; 11(2): 92-102.
- Evid-Based Complement Alt Med 2013; 2013: ID514049, 1-9.