Obesity can result from various factors including diet and is associated with inflammation that often increases with aging. Many ingredients in Proprietary Blend help maintain healthy levels of inflammation including the important olive polyphenols, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein. Obesity is linked with the loss of metabolic energy balance that may be restored by thermogenesis (heat production) from brown fat cells. Olive leaf extract that includes the olive polyphenols, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein have been shown to attenuate or prevent obesity by regulating molecules involved in adipogenesis (fat cell creation) and thermogenesis.
- Many Americans are overweight or obese
- Obesity is part of the metabolic syndrome and is associated with inflammation
- Obesity is linked with many diseases related to chronic inflammation and is also related to an energy imbalance
- Proprietary Blend consists of many antioxidant ingredients including olive polyphenols that help maintain healthy levels of inflammation
- Olive leaf extract that includes olive polyphenols attenuates or prevents obesity in models where obesity is induced by high-fat diets
More than 100 million Americans are overweight or obese. In other words, 65% of the adult population has a weight problem. Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2. BMI is based on the fact that body weight is proportional to the square height of adults with normal body frames. 35% of men and 40.4% of women in the United States are obese according to a recent U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey1.
Obesity can result from various factors or combinations of factors including genetics, lifestyle, diet, lack of exercise and/or sleep and certain medical conditions2,3. It is considered part of the metabolic syndrome that often precedes diabetes4, and it is associated with abnormalities in lipid and glucose metabolism, chronic inflammation and oxidative stress5. In addition, it is linked with an increased risk in several diseases including cardiovascular disease and cancers that have also been linked with chronic inflammation3,5. Moreover, low-grade inflammation is associated with aging that can lead to impaired insulin signaling and weight gain6.
Proprietary Blend Supports Important Metabolic Activities
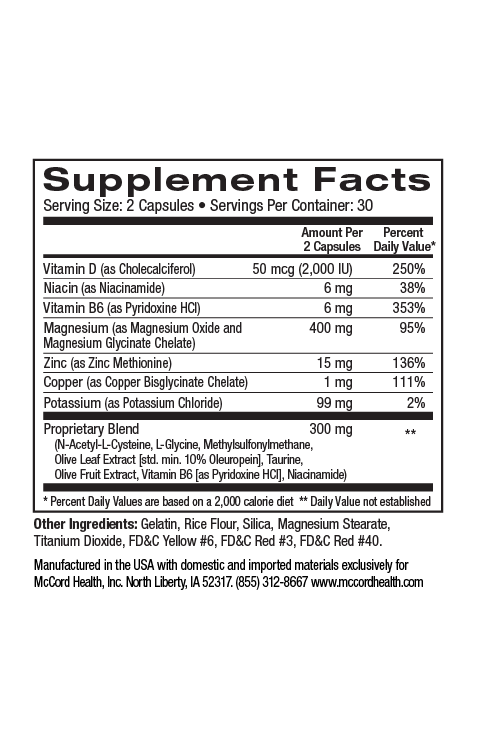
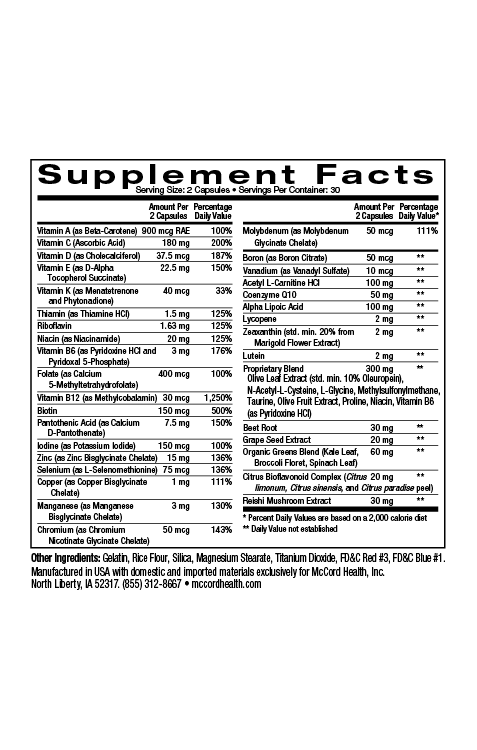
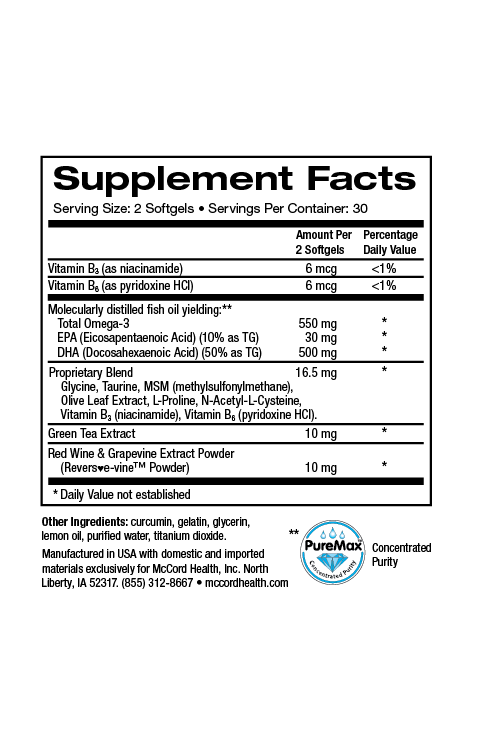
The olive polyphenols, oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol that are vital components of Proprietary Blend have powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. In addition, other key components of Proprietary Blend have important anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities including taurine, N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and methylsulfonylmethane7-16. Proprietary Blend EnergySupport includes caffeine that also has anti-inflammatory activity, and Proprietary Blend VitalBoost includes vitamin D and magnesium, which have been shown to have important anti-inflammatory activity. Moreover, Proprietary Blend includes critical amino acids and vitamins to support important metabolic activities.
Obesity is linked with an energy imbalance whereby energy intake exceeds energy use. This results in the accumulation of white adipose (fat) tissue17. Adipogenesis is the process in which fat cells are formed2. In contrast to white fat, mitochondrial-rich brown fat that decreases with aging is important for energy balance17,18. Brown fat dissipates energy in the form of heat during a process called thermogenesis, which is activated by cellular mechanisms in response to exercise, diet or cold exposure2,17.
Mitochondria, the powerhouses of cells that produce energy in the form of a molecule known as ATP, play a key role in thermogenesis17. Hydroxytyrosol conveys beneficial effects on mitochondrial biogenesis (creation) and it protects mitochondria from damage and dysfunction17,19. NAC has also been found to protect mitochondria from damage20. Olive leaf extract that contains olive polyphenols including oleuropein and hydroxtyrosol, has been shown to attenuate or prevent obesity by regulating molecules involved in adipogenesis and thermogenesis in models where obesity was induced by high-fat diets2,17.
Olive Polyphenols Convey Beneficial Effects Against Obesity
Olive polyphenols including hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein reduce risk factors for metabolic syndrome4. In addition, these olive polyphenols have been found to convey beneficial effects against obesity17. Extra-virgin olive oil that includes these important olive polyphenols was also found to reduce adipose tissue hypertrophy (enlargement) and inflammation21. In fact, oleuropein supplementation prevented obesity in a model in which obesity was induced by a high fat diet17. Furthermore, hydroxytyrosol has been shown to reverse the induction of obesity and insulin resistance by modulating gut microbiota in a model where obesity was also generated by a high-fat diet. In addition, evidence suggests that a high-fat diet increases intestinal permeability to toxins that induce inflammation. Moreover, previous research by this group indicated that hydroxytyrosol reduced inflammation in the same model of obesity3.
EnergyBoost and VitalBoost with Proprietary Blend http://www.olivamine.com include important ingredients to support critical cellular processes including energy metabolism. Hydroxytyrosol increases mitochondrial biogenesis and along with N-acetylcysteine protects mitochondria from damage and dysfunction. In addition, the olive polyphenols, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein as well as key supporting ingredients decrease oxidative stress and inflammation associated with obesity. VitalBoost also includes Vitamin D3 and magnesium to further support cellular processes and decrease inflammation. Importantly, vitamin D has been shown to help reduce obesity and evidence suggests that hydroxytyrosol and vitamin D support intestinal barrier integrity3,22. EnergyBoost and Vital Boost include impeccably sourced ingredients that have undergone rigorous scientific review to prove we renew, restore and repair cells.
References
- Endocrine Rev 2018; 39(2): 79-132.
- In Vivo 2019; 33: 707-715.
- Front Microbiol 2019; 10: 390: 1-12.
- Molecules 2017; 22: 1082, 1-15.
- Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 1146, 1-18.
- Cell Metabol 2017; 25: 506-521.
- J Agric Food Chem 2011; 59: 4473-4482.
- Sci Pharm 2010; 78: 133-154.
- Amino Acids 2004; 26: 203-207.
- Nutrients 2017; 9(3): 290, 1-21.
- Life Sci 2015; 121: 110-116.
- Planta Med 2011; 77: 1890-1897.
- Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: 18508-18524.
- World J Diabetes 2014; 5: 679-710.
- Biol Pharm Bull 2009; 32: 651-656.
- Amino Acids 1996; 10: 59-71.
- Evid-Based Compl Alt Med 2014; 2014: ID 971890, 1-12.
- Front Endocrinol 2019; 10: 137, 1-12.
- Age 2012; 34: 95-109.
- Mitochondrion 2010; 10(4): 342-349.
- Mol Nutr Food Res 2018; 62(13): e1800295.
- Biomol Ther 2019; 27(2): 222-230.