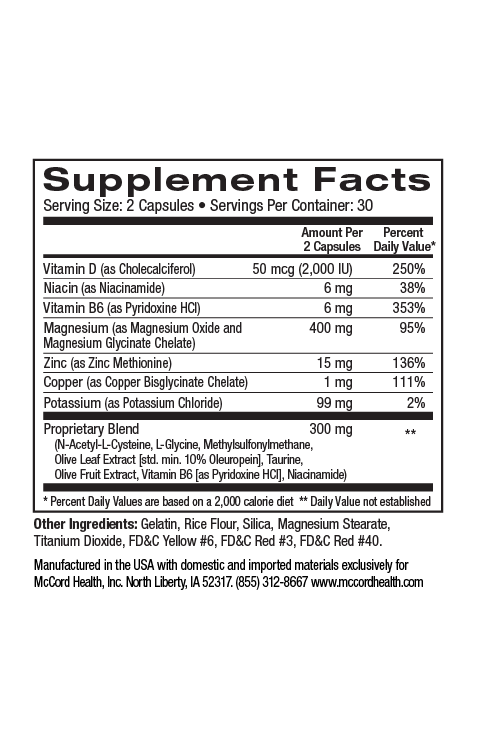
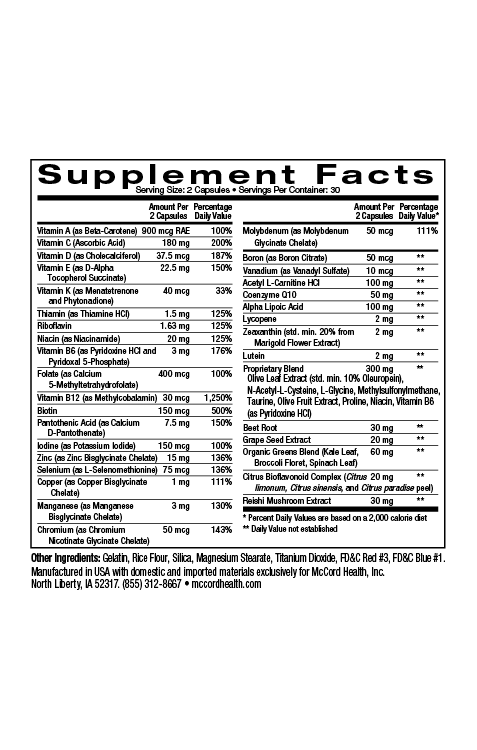
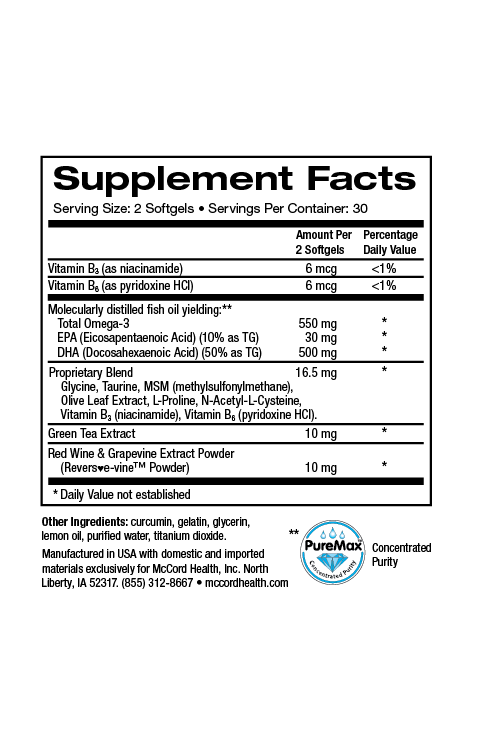
The Mediterranean diet that is characterized by a high consumption of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is associated with increased mental and brain health. EVOO contains higher levels of the olive polyphenols hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein that are also found in Proprietary Blend. EVOO consumption corresponds with decreased symptoms of depression and anxiety as well as increased neuroprotection. Magnesium (found in CalmMind) has been shown to decrease inflammation that has been linked with depression. Hydroxytyrosol has been shown to improve decision-making and decrease anxiety-like behavior and is anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective along with several other ingredients found in Proprietary Blend and CalmMind.
- Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) that has higher content of olive polyphenols is associated with decreased symptoms of depression and anxiety
- Depression is associated with increased inflammation
- Many of the beneficial small molecules in Proprietary Blend as well as magnesium and curcumin found in CalmMind can help decrease inflammation
- Several of the Proprietary Blend small molecules can cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) and are neuroprotective
The Mediterranean diet is associated with various positive attributes including increased mental and brain health. This amazingly nutritious diet is characterized by a high consumption of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) and includes olive fruits. EVOO has been shown to contain higher levels of olive polyphenols including hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein found in Proprietary Blend that have been shown to convey many of the health benefits of olive oil and the Mediterranean diet1,2.
Many studies have found that adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with decreased depression3. Further, EVOO consumption has been associated with decreased symptoms of depression and anxiety, as well as increased mental functioning capacity, neuroprotection and improved health-related psychological status4,5. In fact, an important study revealed that olive oil consumption improved learning and memory, reduced anxiety and increased levels of brain dopamine and serotonin neurotransmitters6.
Decreased Magnesium is Associated with Inflammation and Anxiety
Increased inflammation has been associated with many health issues including depression that can be characterized by a long-term depressed mood accompanied by attention and cognitive impairment7-12. Psychological stress has been linked with depression and anxiety as well as inflammation13. Decreased levels of magnesium have been associated with inflammation and increased levels of magnesium (as in Pinnaclife® CalmMind) have been linked with neuroprotection14,15. In addition, the potent olive polyphenols hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein are anti-inflammatory and have also been linked with neuroprotection16-18.
In fact, other critical small molecules found in Proprietary Blend (along with the potent olive polyphenols) are anti-inflammatory including taurine, methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) and N-acetylcysteine(NAC)19-22. Inflammatory molecules in the brain can interfere with neuronal functioning, however, hydroxytyrosol, NAC, MSM and taurine are small molecules that can pass through the blood brain barrier to help protect neurons23-26. Behavioral indications of neuronal cell damage caused by inflammation include decreased physical activity, mood disturbances, anxiety and depression27. Interestingly, hydroxytyrosol was shown to improve decision-making and ameliorate anxiety-like behavior in a model study28.
CalmMind Has Antioxidants That Counteract Oxidative Stress
Clinical studies have also shown that depression is associated with oxidative stress that has been linked with inflammation29,30. Oxidative stress results from the inability of cells to eliminate free radicals known as reactive oxygen species (ROS) using the natural defense system that includes defense enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD)31. Proprietary Blend found in CalmMind includes the potent antioxidants hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein, taurine, NAC and MSM. Notably, hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein and NAC have been shown to activate manganese (Mn) SOD that helps counteract oxidative stress32-34.
Along with Proprietary Blend and magnesium, CalmMind includes curcumin that has important anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities35. Pinnaclife® CalmMind with Proprietary Blend http://www.olivamine.com includes impeccably sourced ingredients that have undergone rigorous scientific review to prove that they renew, restore and repair cells.
References
- Cell Physiol Biochem 2015; 37: 1029-1043.
- Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 2230, 1-27.
- BMC Psychiatry 2019; 19: 63, 1-7.
- Br J Nutr 2010; 103: 1674-1683.
- Biol Res Nurs 2017; 19(1): 106-115.
- J Nutraceuticals Food Sci 2018; 3(1:4): 1-8.
- Curr Opin Rheumatol 2015; 27: 249-255.
- Curr Opin Rheumatol 2015; 27: 289-294.
- Mol Cells 2014; 37: 441-448.
- Free Radic Biol Med 2010; 49: 1603-1616.
- Neurotox Res 2013; 23: 131-144.
- Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2012; 39: 280-287.
- J Psychiatr Res 2015; 63: 65-74.
- Nutrients 2018; 10:730: 1-23.
- J Inflamm Res 2018; 11: 25-34.
- Planta Med 2011; 77: 1890-1897.
- Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: 18508-18524.
- Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 2230, 1-27.
- Biochem Biophys Res Comm 2104; 466: 1225-1230.
- Biol Pharm Bull 2009; 32: 651-656.
- Amino Acids 1996; 10: 59-71.
- Foods 2017; 6(10):92: 1-11.
- Adv Exp Med Biol 2013; 175: 19-27.
- J Biomed Sci 2017; 24: 71: 1-15.
- J Prev Alzheimers Dis 2017; 4(3): 201-206.
- Nutrients 2017; 9: 290: 1-21.
- Front Cell Neurosci 2015; 9: 1-20.
- ACS Chem Neurosci 2018; 9(12): 2904-2916.
- Pharmacol Rep 2013; 65: 1558-1571.
- J Clin Diagnostic Res 2014; 8: 4-7.
- Curr Neuropharmacol 2009; 7: 65-74.
- Cancer Res 2007; 67: 6392-6399.
- Age 2012; 34: 95-109.
- J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2014; 28: 105-116.
- Neurochem Res 2014; 39(7): 1322-1331.