For centuries, aloe vera has been prized for its medicinal properties that include the enhancement of skin health and healing. In fact, aloe plants have been used for over 2000 years in the treatment of skin diseases; ancient Egyptians called it “the plant of immortality” and early Greek physicians considered it a universal panacea.
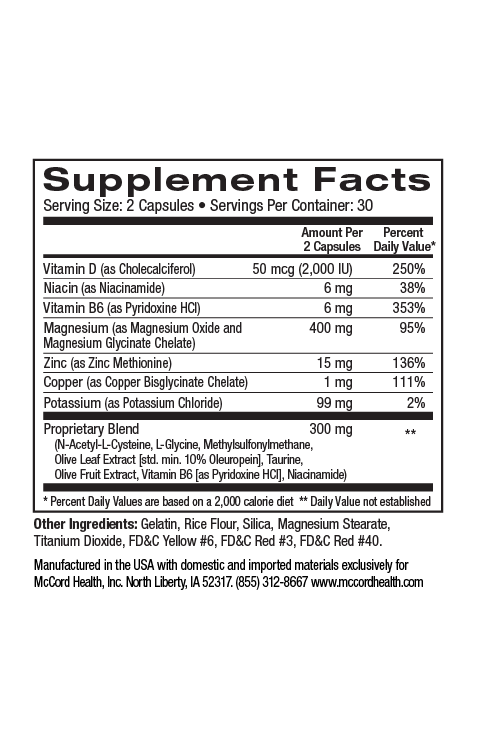
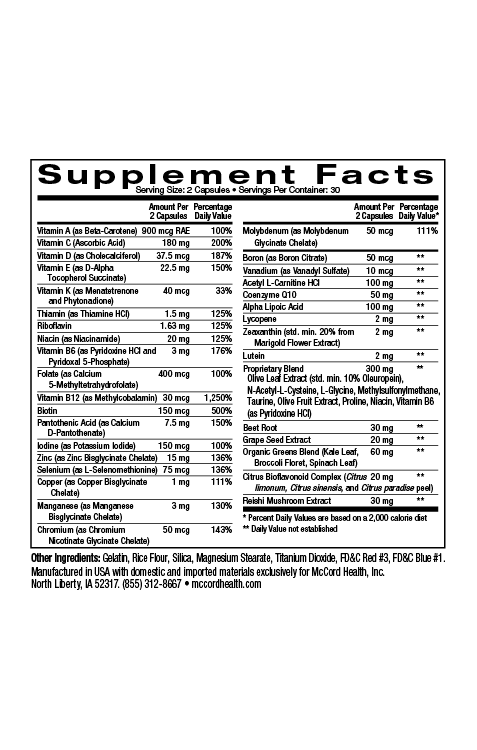
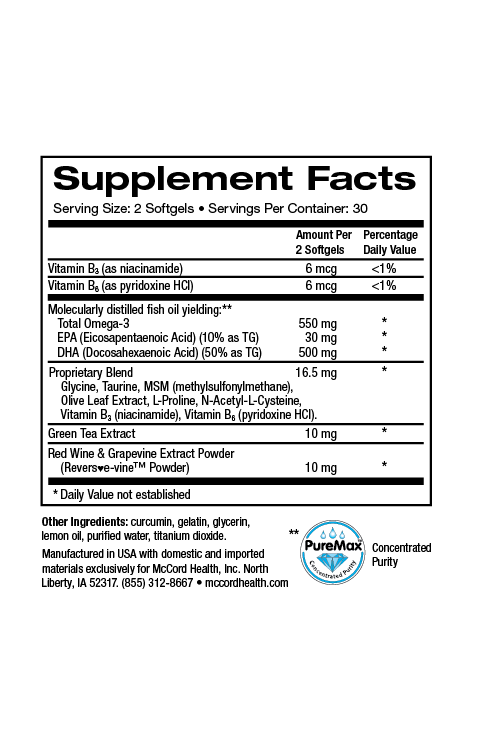
Aloe vera contains at least 75 components, many of which that are known to promote skin health and wound healing such as beneficial vitamins, minerals and amino acids. Vitamins that come from aloe vera include important B vitamins, vitamin C and vitamin E. Aloe vera also contains amino acids like proline and hydroxyproline that are involved in wound healing. In addition, beneficial minerals found in aloe vera include zinc and calcium that promote wound healing.
Decreasing Inflammation
Along with several other ingredients contained in Viniferamine® skin and wound care products, aloe vera is anti-inflammatory. Other ingredients that are anti-inflammatory include the polyphenols oleuropein, resveratrol, and epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) from olives, grapes, and green tea, respectively, as well as the important small molecules, melatonin, and L-glutathione. In addition, dipotassium glycyrrhizate from licorice, avenanthramides in oats and shea butter possess anti-inflammatory activities.
One of the components of aloe vera that helps make it anti-inflammatory is acemannan, an acetylated polymannose that also has the ability to stimulate the immune system by activating macrophages. In addition, acemannan has antibacterial properties and has been shown to accelerate wound healing. In fact, acemannan has been found to stimulate the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and type I collagen. In addition, aloe vera has also been found to improve keratinocyte function and enhance epidermal development.
Vitamin E and C found in aloe vera also have antioxidant activity that can help protect skin from oxidative stress caused by free radicals known as reactive oxygen species (ROS). In addition, Viniferamine® skin and wound care products like Renewal Moisturizer and Clean N Moist contain other important antioxidants including the potent small molecules, oleuropein, resveratrol and EGCG, as well as the powerful small molecules melatonin and L-glutathione.
Promoting Wound Healing and Hydration and Decreasing Photodamage
Aloe vera has been used successfully to treat burn injuries and surgical scars and has critical skin hydrating properties. Importantly, aloe vera has been shown to increase levels of hyaluronic acid (HA), a large glycosaminoglycan (GAG) with a molecular weight as high as 5 million kDa. Due to its large size and positive charge, HA is capable of binding up to 1000 times its weight in water. GAGs comprise a substantial portion of the extracellular matrix (ECM), which is composed of molecules (secreted by cells) that provide structural and biochemical cellular support. HA is found in all tissues of the human body, but is most abundant in the skin and like other ECM components is critical in the regulation of all stages of wound repair including cellular migration, inflammation and remodeling.
Finally, aloe vera has been shown to protect against photodamage caused by UV radiation. Other ingredients found in Viniferamine® skin and wound care products also have protective properties against UV damage including EGCG, resveratrol and oleuropein. EGCG has been shown to counteract the detrimental effects of UV radiation on immunity. Resveratrol has been shown to protect human skin from damage induced by repeated exposure to UV radiation. In addition, photoprotection has been found with increased levels of the enzyme, heme oxygenase that is induced by oleuropein. Moreover, two other beneficial ingredient found in Viniferamine® skin and wound care products, melatonin and niacinamide (nicotinamide) exert strong protective effects against UV-induced skin damage and immunosuppression, respectively.
It’s good to know that Viniferamine® skin and wound care products contain aloe vera to enhance skin health and wound healing due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antibacterial activities, as well as its ability to activate the immune system and stimulate collagen production. Moreover, aloe vera helps keep skin hydrated and is photoprotective.
About the author: Nancy Ray, PhD is the Science Officer at McCord Research. Dr. Ray received her PhD in Biochemistry and Biophysics and was a postdoctoral fellow at NIH, Harvard University and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and the University of Iowa. She also earned bachelor of science degrees in Chemistry and Microbiology.
References
- Ind J Dermatol 2008; 53: 163-166.
- Br J Gen Pract 1999; 49: 823-828.
- Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: 18508-18524.
- Diab Vasc Dis Res 2014; 11: 92-102.
- Oxid Med Cell Longev 2012; ID 560682:1-8.
- J Pineal Res 2013; 55: 325-356.
- Int J Gen Med 2011; 4: 105-113.
- Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2012; ID 650514:1-9.
- Cell J 2014; 16: 25-30.
- ISRN Endicronol 2014; ID 816307: 1-8.
- J Am Acad Dermatol 2005; 52: 1049-1059.
- Int J Immunopharmac 1997; 19: 75-82.
- Nat Prod Commun 2014; 9: 1217-1221.
- J Pharmacol Sci 2009; 109: 525-531.
- Adv Wound Care 2016; 5: 208-229.
- Ann Plast Surg 2016; 77: 37-46.
- Altern Med Rev 2003; 8: 359-377.
- J Ethnopharmacol 1998; 59: 179-186.
- Molecules 2014; 19: 6202-6219.
- Photochem Photobiol 2012; 88: 1083-1098.
- Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: 17705-17732.
- Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2014; 30: 112-127.
- Int J Mol Sci 2013; 14: 1964-1977.
- Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2017; 33: 101-111.
Disclaimer: These statements have not been reviewed by the FDA. The decision to use these products should be discussed with a trusted healthcare provider. The authors and the publisher of this work have made every effort to use sources believed to be reliable to provide information that is accurate and compatible with the standards generally accepted at the time of publication. The authors and the publisher shall not be liable for any special, consequential, or exemplary damages resulting, in whole or in part, from the readers’ use of, or reliance on, the information contained in this article. The publisher has no responsibility for the persistence or accuracy of URLs for external or third party Internet websites referred to in this publication and does not guarantee that any content on such websites is, or will remain, accurate or appropriate.