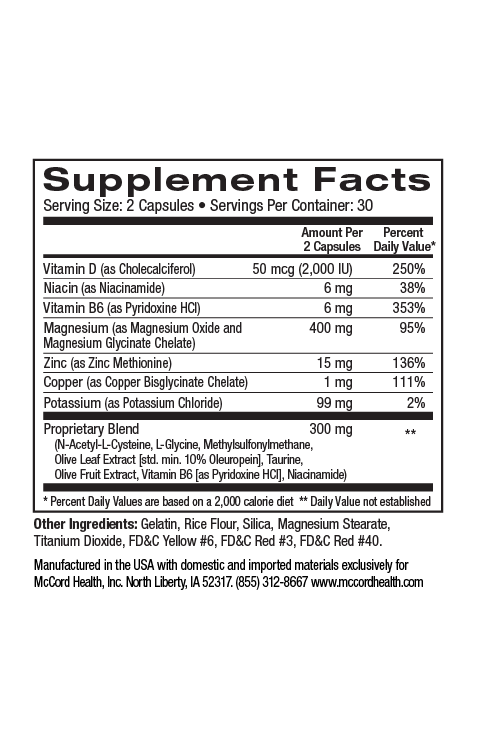
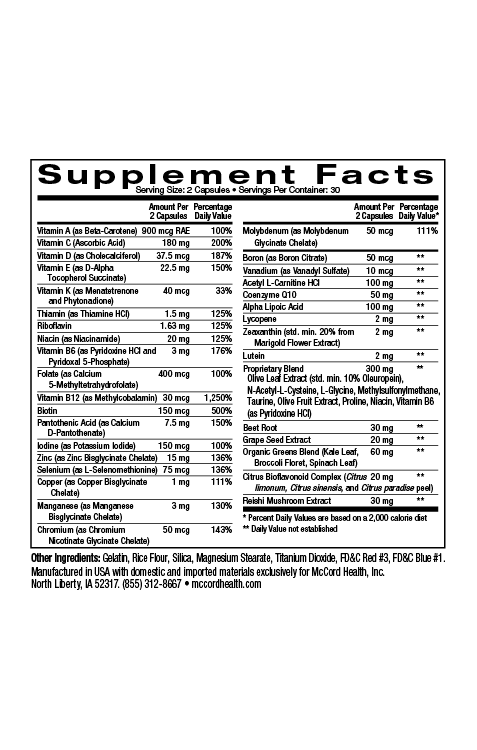
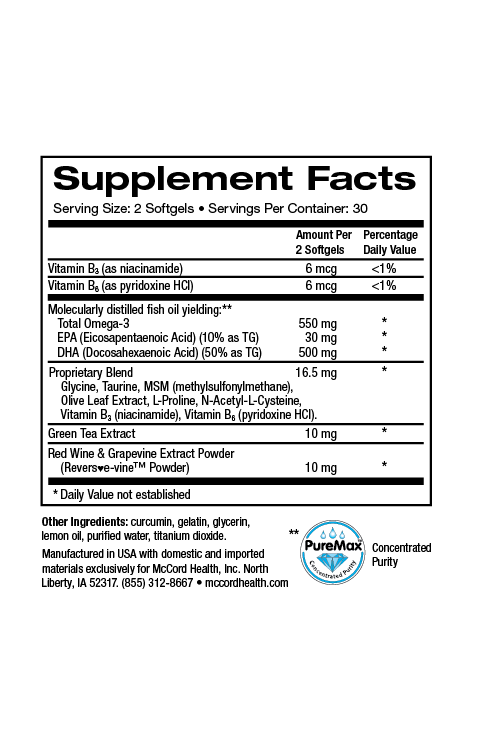
According to recent estimates, at least 35% of Americans are classified as obese, and this trend towards obesity is only increasing. Obesity is defined as a state of excess adiposity (accumulation of lipids) due to prolonged positive energy imbalance. Obesity is also defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30kg/m or greater. There are multiple causes for obesity including, diet, genetics, inactivity or weight gain related to drugs such as oral corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, or serotonin reuptake inhibitors (antidepressants). Obesity increases the risk involved with more than 30 medical problems including skin issues.
Obesity is associated with oxidative stress and inflammation that can have deleterious affects on the skin resulting in decreased skin barrier function, decreased skin immunity, and decreased wound healing. In fact, many skin issues related to oxidative stress and/or inflammation are frequently associated with obesity including stasis dermatitis, intertrigo (inflammation in skin folds), striae (stretch marks), folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles), xerosis (dry skin) and psoriasis. Furthermore, increased inflammation and obesity is typically linked with diabetes that can lead to diabetic foot ulcers, or prolonged inflammation associated with stasis dermatitis that can result in stasis (venous) ulcers.
Viniferamine® skin and wound care products contain potent anti-inflammatory ingredients including the polyphenols oleuropein, resveratrol, and epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) from olives, grapes, and green tea, respectively, as well as the important small molecules, melatonin, and L-glutathione. In addition, dipotassium glycyrrhizate from licorice, avenanthramides in oats, aloe vera and shea butter possess anti-inflammatory activities. Viniferamine products also contain important ingredients that counteract oxidative stress including oleuropein, resveratrol, and EGCG, as well as melatonin, and L-glutathione.
Increased inflammation can also result in pruritus (itching) and burning sensations frequently corresponding with obesity-related skin conditions including psoriasis, xerosis and folliculitis. The many anti-inflammatory ingredients found in Viniferamine® skin and wound care products can help decrease inflammation. In fact, Viniferamine® Renewal Moisturizer and Silicone Barrier can help decrease redness, itching, inflammation and burning sensations.
Obesity also decreases blood and lymphatic circulation leading to poor skin nutrition (since fewer nutrients are provided from the blood) and edema that can increase skin breakdown, increase the risk of venous stasis, promote immune dysfunction and impair wound healing. Viniferamine® skin and wound care products contain small molecule skin nutrients including antioxidants, amino acids and vitamins that can penetrate the epidermis to provide nutrition to skin. Viniferamine® SkinMineralZ also provides important skin minerals from mineral-rich clays as well as zinc oxide, and can absorb toxins and excess moisture associated with maceration and skin breakdown.
Decreased skin barrier function and increased skin pH has also been associated with obesity. Abnormal skin pH can result in dysbiosis (an upset in the natural balance of skin microorganisms or microbiome), which may lead to the increased growth of certain bacteria and fungi that can become pathogenic, including Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Candida albicans (C. albicans). In fact, a higher skin pH encourages the growth of C. albicans. In addition, excess moisture (that also encourages its growth) from sweating that may be found in skin folds often results in intertrigo due to irritation and friction from rubbing skin that can also contribute to skin breakdown.
Viniferamine® skin and wound care products including Renewal Moisturizer and Clean N Moist contain ingredients that strengthen the skin barrier such as oleuropein, which has been shown to increase barrier function and melatonin, which has been shown to have a stimulatory role in building and maintaining the epidermal barrier. All of the products are pH balanced to help preserve the natural skin microbiome and pH. In fact, the chemistry of the mild skin cleanser, Clean N Moist, corresponds with the chemistry of skin to ensure that at-risk skin is gently cleansed without causing irritation. Renewal Moisturizer and Clean N Moist also contain skin-hydrating ingredients as well as skin nutrients that help decrease xerosis and skin breakdown.
Many skin infections are more problematic with obesity including skin infections associated with folliculitis, cellulitis, and surgical sites. Viniferamine® Antiseptic Cleanser helps decrease the risk of microbial skin contamination, and contains a gentle broad-spectrum antimicrobial ingredient found in many eye drops, and along with other Viniferamine products, contains many naturally antimicrobial ingredients including resveratrol, which has been reported to inhibit methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), and EGCG, which was shown to have antimicrobial effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Oleuropein has also been shown to inhibit the growth of several bacterial strains including S. aureus, and melatonin, has antimicrobial effects against MRSA and antibiotic resistant P. aeruginosa. In addition, Viniferamine® Silicone Barrier provides a “breathable” protective barrier to help exclude skin contaminants and irritants, and prevent friction due to rubbing skin. Silicone Barrier also includes an antimicrobial to decrease the risk of infections.
The ability of skin fibrobasts to produce collagen required for wound healing is also affected by obesity. Decreased oxygenation of tissues due to obesity that results from decreased blood circulation and other factors, inhibits their ability to synthesize collagen properly. Viniferamine® skin and wound care products contain ingredients that promote collagen synthesis and wound healing including titrated extract of Centella asiatica (TECA) and aloe vera. With obesity, impaired wound healing and skin breakdown can also be related to an individual’s immobility or sedation, as well as improperly sized equipment such as wheelchairs that contribute to chronic wounds such as pressure ulcers.
Because obesity is associated with an increased risk of skin issues including skin breakdown, wounds and infections, skin (especially in skin fold areas) should be carefully examined and monitored for moisture, inflammation and signs of infection such as redness, swelling, warmth, or odor. Areas between skin folds should also be kept clean and dry. Viniferamine® SkinMineralZ can help absorb excess moisture and irritating toxins from sweat. Other areas including feet should be examined carefully, moisturized (except between toes) and protected to prevent skin breakdown and ulcers.
It’s good to know that Viniferamine® skin and wound care products help protect skin at risk due to health issues such as obesity. Viniferamine® skin and wound care products include potent anti-inflammatory ingredients, as well as other beneficial ingredients that counteract oxidative stress, help preserve a healthy skin pH and microbiome, decrease the risk of irritations and infections, and strengthen skin to help prevent skin breakdown and promote wound healing.
About the author: Nancy Ray, PhD is the Science Officer at McCord Research. Dr. Ray received her PhD in Biochemistry and Biophysics and was a postdoctoral fellow at NIH, Harvard University and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and the University of Iowa. She also earned bachelor of science degrees in Chemistry and Microbiology.
References
- Endocrinol Metab Synd 2013; 2: 1-9.
- ISRN Obesity 2014; ID 638936: 1-13.
- Ostomy Wound Manag 2014; 60: 12-21.
- J Am Acad Dermatol 2007; 56: 901-916.
- Ostomy Wound Manag 2006; 52: 34-47.
- Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: 18508-18524.
- Diab Vasc Dis Res 2014; 11: 92-102.
- Oxid Med Cell Longev 2012; ID 560682:1-8.
- J Pineal Res 2013; 55: 325-356.
- Int J Gen Med 2011; 4: 105-113.
- Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2012; ID 650514:1-9.
- Cell J 2014; 16: 25-30.
- ISRN Endicronol 2014; ID 816307: 1-8.
- J Am Acad Dermatol 2005; 52: 1049-1059.
- Ann Plast Surg 2007; 58: 449-455.
- PLOS One 2015; 10: e0115341: 1-18.
- Exp Dermatol 2008; 17: 713-730.
- Clin Dermatol 2004; 22: 303-309.
- Bariatric Times 2008 (June 11); 1-7.
- J Obes Weight-Loss Medic 2016; 1: 1-7.
- Sci Rep 2014; 4: 5467:DOI: 10.1038/srep05467.
- Sci Rep 2015; 5: 16158: DOI: 10.1038/srep16158.
- Br J Pharmacol 2013; 168: 1059-1073.
- Z Naturforsch 2003; 168: 1059-1073.
- J Pharm Pharmacol 1999; 51: 971-974.
- J Pineal Res 2008; 44: 222-226.
- Connect Tissue Res 1990; 24: 107-120.
- BMC Compl Altern Med 2012; 12: 103-120.
- Altern Med Rev 2003; 8: 359-377.
Disclaimer: These statements have not been reviewed by the FDA. The decision to use these products should be discussed with a trusted healthcare provider. The authors and the publisher of this work have made every effort to use sources believed to be reliable to provide information that is accurate and compatible with the standards generally accepted at the time of publication. The authors and the publisher shall not be liable for any special, consequential, or exemplary damages resulting, in whole or in part, from the readers’ use of, or reliance on, the information contained in this article. The publisher has no responsibility for the persistence or accuracy of URLs for external or third party Internet websites referred to in this publication and does not guarantee that any content on such websites is, or will remain, accurate or appropriate.